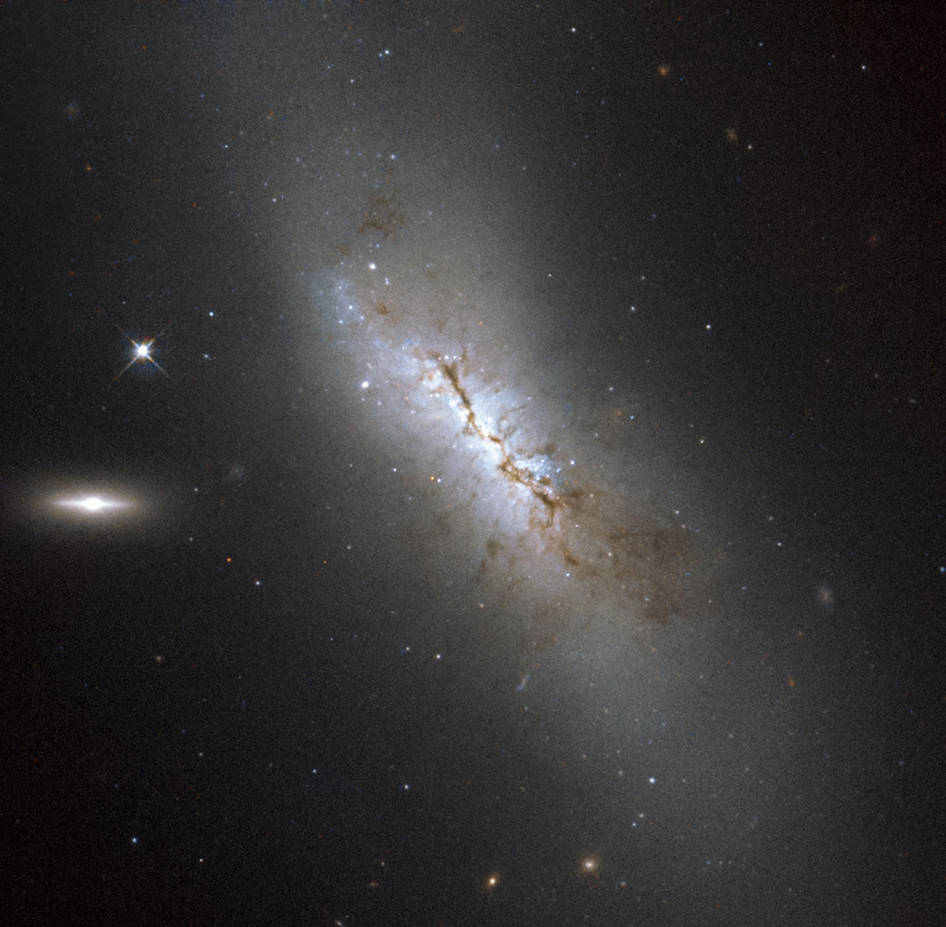
The galaxy NGC 4424, located in the constellation of Virgo which is not visible with the naked eye has been captured with the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope.
Although it may not be obvious from this image, NGC 4424 is in fact a spiral galaxy. In this image it is seen more or less edge on, but from above, you would be able to see the arms of the galaxy wrapping around its center to give the characteristic spiral form.
In 2012, astronomers observed a supernova in NGC 4424 — a violent explosion marking the end of a star’s life. During a supernova explosion, a single star can often outshine an entire galaxy. However, the supernova in NGC 4424, dubbed SN 2012cg, cannot be seen here as the image was taken ten years prior to the explosion. Along the central region of the galaxy, clouds of dust block the light from distant stars and create dark patches.
To the left of NGC 4424 there are two bright objects in the frame. The brightest is another, smaller galaxy known as LEDA 213994 and the object closer to NGC 4424 is an anonymous star in our Milky Way.