High-speed experiments will help identify lightweight, protective “metamaterials” for spacecraft, vehicles, helmets, or other objects.
CAMBRIDGE, MA – An intricate, honeycomb-like structure of struts and beams could withstand a supersonic impact better than a solid slab of the same material. What’s more, the specific structure matters, with some being more resilient to impacts than others.
That’s what MIT engineers are finding in experiments with microscopic metamaterials — materials that are intentionally printed, assembled, or otherwise engineered with microscopic architectures that give the overall material exceptional properties.
In a study appearing today in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, the engineers report on a new way to quickly test an array of metamaterial architectures and their resilience to supersonic impacts.
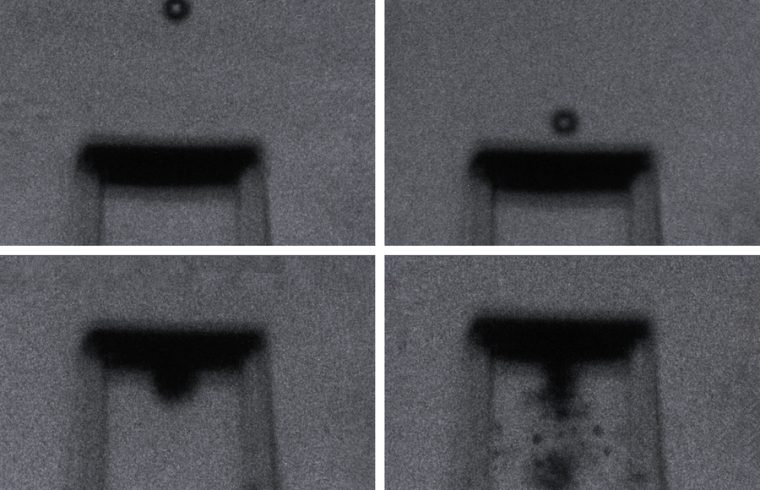
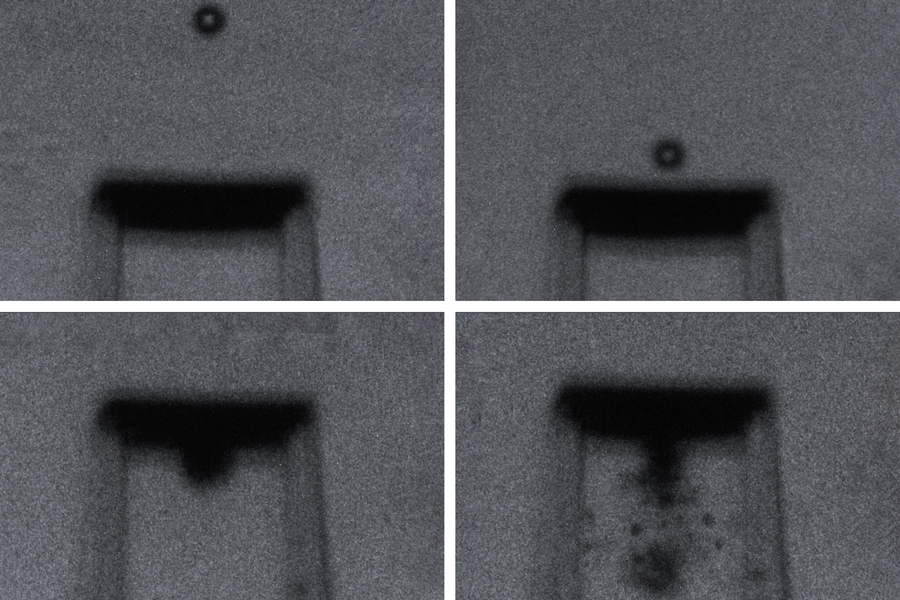
In their experiments, the team suspends tiny printed metamaterial lattices between microscopic support structures, then fires even tinier particles at the materials, at supersonic speeds. With high-speed cameras, the team then captures images of each impact and its aftermath, with nanosecond precision.
Their work has identified a few metamaterial architectures that are more resilient to supersonic impacts compared to their entirely solid, nonarchitected counterparts. The researchers say the results they observed at the microscopic level can be extended to comparable macroscale impacts, to predict how new material structures across length scales will withstand impacts in the real world.
“What we’re learning is, the microstructure of your material matters, even with high-rate deformation,” says study author Carlos Portela, the Brit and Alex d’Arbeloff Career Development Professor in Mechanical Engineering at MIT. “We want to identify impact-resistant structures that can be made into coatings or panels for spacecraft, vehicles, helmets, and anything that needs to be lightweight and protected.”
Other authors on the study include first author and MIT graduate student Thomas Butruille, and Joshua Crone of DEVCOM Army Research Laboratory.
Pure impact
The team’s new high-velocity experiments build off their previous work, in which the engineers tested the resilience of an ultralight, carbon-based material. That material, which was thinner than the width of a human hair, was made from tiny struts and beams of carbon, which the team printed and placed on a glass slide. They then fired microparticles toward the material, at velocities exceeding the speed of sound.
Those supersonic experiments revealed that the microstructured material withstood the high-velocity impacts, sometimes deflecting the microparticles and other times capturing them.
“But there were many questions we couldn’t answer because we were testing the materials on a substrate, which may have affected their behavior,” Portela says.
In their new study, the researchers developed a way to test freestanding metamaterials, to observe how the materials withstand impacts purely on their own, without a backing or supporting substrate.
In their current setup, the researchers suspend a metamaterial of interest between two microscopic pillars made from the same base material. Depending on the dimensions of the metamaterial being tested, the researchers calculate how far apart the pillars must be in order to support the material at either end while allowing the material to respond to any impacts, without any influence from the pillars themselves.
“This way, we ensure that we’re measuring the material property and not the structural property,” Portela says.
Once the team settled on the pillar support design, they moved on to test a variety of metamaterial architectures. For each architecture, the researchers first printed the supporting pillars on a small silicon chip, then continued printing the metamaterial as a suspended layer between the pillars.
“We can print and test hundreds of these structures on a single chip,” Portela says.
Punctures and cracks
The team printed suspended metamaterials that resembled intricate honeycomb-like cross-sections. Each material was printed with a specific three-dimensional microscopic architecture, such as a precise scaffold of repeating octets, or more faceted polygons. Each repeated unit measured as small as a red blood cell. The resulting metamaterials were thinner than the width of a human hair.
The researchers then tested each metamaterial’s impact resilience by firing glass microparticles toward the structures, at speeds of up to 900 meters per second (more than 2,000 miles per hour) — well within the supersonic range. They caught each impact on camera and studied the resulting images, frame by frame, to see how the projectiles penetrated each material. Next, they examined the materials under a microscope and compared each impact’s physical aftermath.
“In the architected materials, we saw this morphology of small cylindrical craters after impact,” Portela says. “But in solid materials, we saw a lot of radial cracks and bigger chunks of material that were gouged out.”
Overall, the team observed that the fired particles created small punctures in the latticed metamaterials, and the materials nevertheless stayed intact. In contrast, when the same particles were fired at the same speeds into solid, nonlatticed materials of equal mass, they created large cracks that quickly spread, causing the material to crumble. The microstructured materials, therefore, were more efficient in resisting supersonic impacts as well as protecting against multiple impact events. And in particular, materials that were printed with the repeating octets appeared to be the most hardy.
“At the same velocity, we see the octet architecture is harder to fracture, meaning that the metamaterial, per unit mass, can withstand impacts up to twice as much as the bulk material,” Portela says. “This tells us that there are some architectures that can make a material tougher which can offer better impact protection.”
Going forward, the team plans to use the new rapid testing and analysis method to identify new metamaterial designs, in hopes of tagging architectures that can be scaled up to stronger and lighter protective gear, garments, coatings, and paneling.
“What I’m most excited about is showing we can do a lot of these extreme experiments on a benchtop,” Portela says. “This will significantly accelerate the rate at which we can validate new, high-performing, resilient materials.”
This work was funded in part by DEVCOM ARL Army Research Office through the MIT Institute for Soldier Nanotechnologies (ISN).