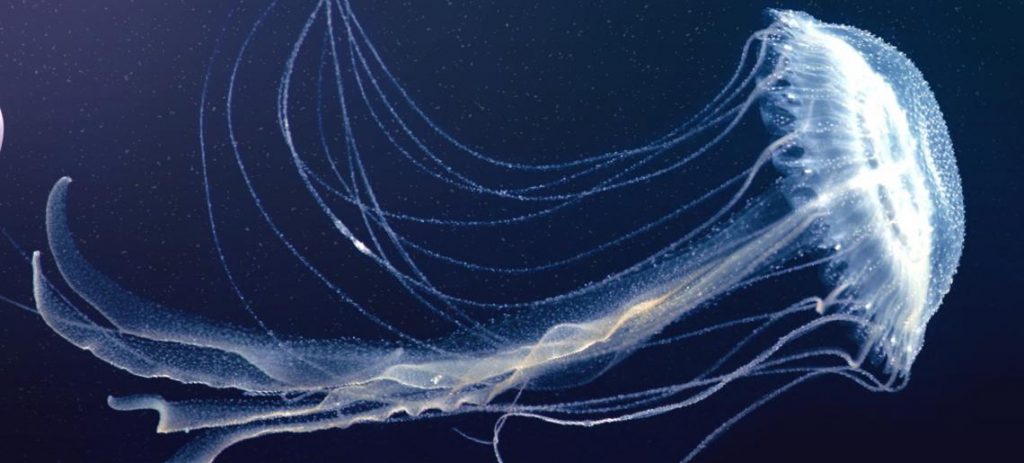
A research team led by Professor Jerome HUI Ho Lam from the School of Life Sciences at The Chinese University of Hong Kong (CUHK) has decoded for the first time the high-quality genomes of two jellyfish commonly found in Asian waters, including the edible flame jellyfish. It helps to unveil its ecological roles and reproduction mechanism.
Further studies have revealed many unexpected biological findings, including the identification of hormones which are thought to be only contained in arthropods like insects. The findings, just published in Nature Communications, provide references for further studies on the evolution, ecological roles and population bloom of jellyfish.
Jellyfish are found in every major ocean in the world, from surface waters to the deep sea. They play an important role in the oceanic food chain. Several species of jellyfish have also been adopted as a food source in some Asian regions. However, factors like climate change and ocean eutrophication have promoted high frequencies in jellyfish bloom, which, in turn, are responsible for negative effects on human activities and the marine ecosystem. Jellyfish swarms sting thousands of swimmers, clog the cooling systems of power stations and damage fishing apparatus.
Jellyfish have myriads of characteristics and shapes. Some of them glitter, some of them can be reborn, some can reproduce both asexually and sexually, and some of them do not have circular bells until adulthood. Very little is known about the factors that regulate their transformation.
To better understand their hidden biology, Prof. Hui and his team sequenced the genomes of two species of jellyfish which can be found in Asian seawaters including Hong Kong. They are the Amuska jellyfish Sanderia malayensis and the edible jellyfish Rhopilema esculentum, also known as flame jellyfish, which is regarded as a delicacy in China and some South East Asian countries.
The team has identified several unexpected findings ranging through genome architecture, development, noncoding RNAs, to evolution. A highlight finding is that the genes that encode sesquiterpenoid hormones, including family members of the well-known juvenile hormone in insects, are for the first time discovered to be present in jellyfish. Sesquiterpenoid hormones are important in regulating metamorphosis in arthropods like insects, e.g. the moult and wing growth of the silkworm. Since jellyfish also undergo metamorphosis during their life cycle, this finding would help scientists to understand how jellyfish undergo the transition between developmental stages, and the change of reproduction method during their lifecycle.
Another key finding is the distinct homeobox genes organisation in the two-germ layers jellyfish to that of three-germ layers bilaterians, including humans. Homeobox genes are important development regulators for the formation of three germ layers in bilaterians (ectoderm – skin and nervous system, endoderm – gut, mesoderm – muscle).
Cnidarians like jellyfish only have two germ layers, but contain most of the three germ layer homeobox genes. The team has now identified distinct homeobox gene organisation in two jellyfishes, showing the cnidarians and bilaterians have undergone different pathways since their extinct cnidarian-bilaterian ancestor of more than 600 million years before.Professor Hui stated, “Jellyfish is one of the most fascinating marine creatures.
This curious looking animal has myriads of characteristics and ecological features, which are worth studying by marine scientists. Our team will further explore its mechanism on both evolution and development, understand the functions of the newly discovered hormones in these cnidarians, and examine new methods in response to the threat brought by jellyfish bloom and climate change”.