ESA—Dark clouds, the smell of rain on a hot sidewalk, the flashes of intense light followed by a loud crackling and then a low, rolling thunder – who doesn’t love a good summer thunderstorm. We’ve all seen one, heard one, or been completely soaked by one. But how much do we really know about this weather phenomenon?
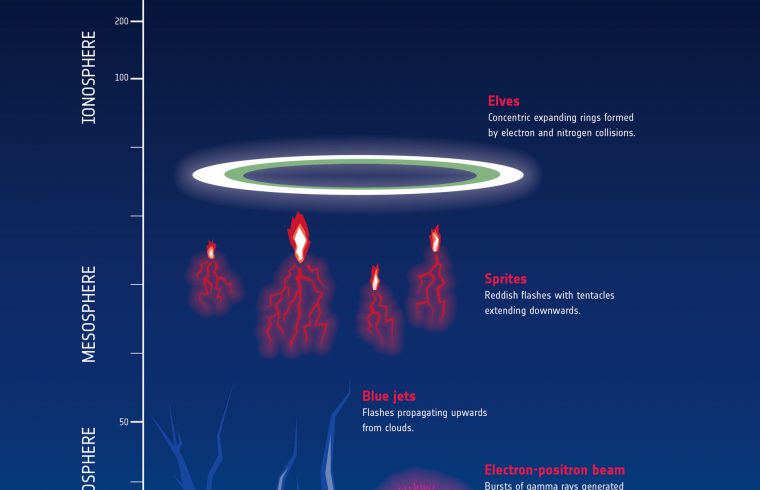
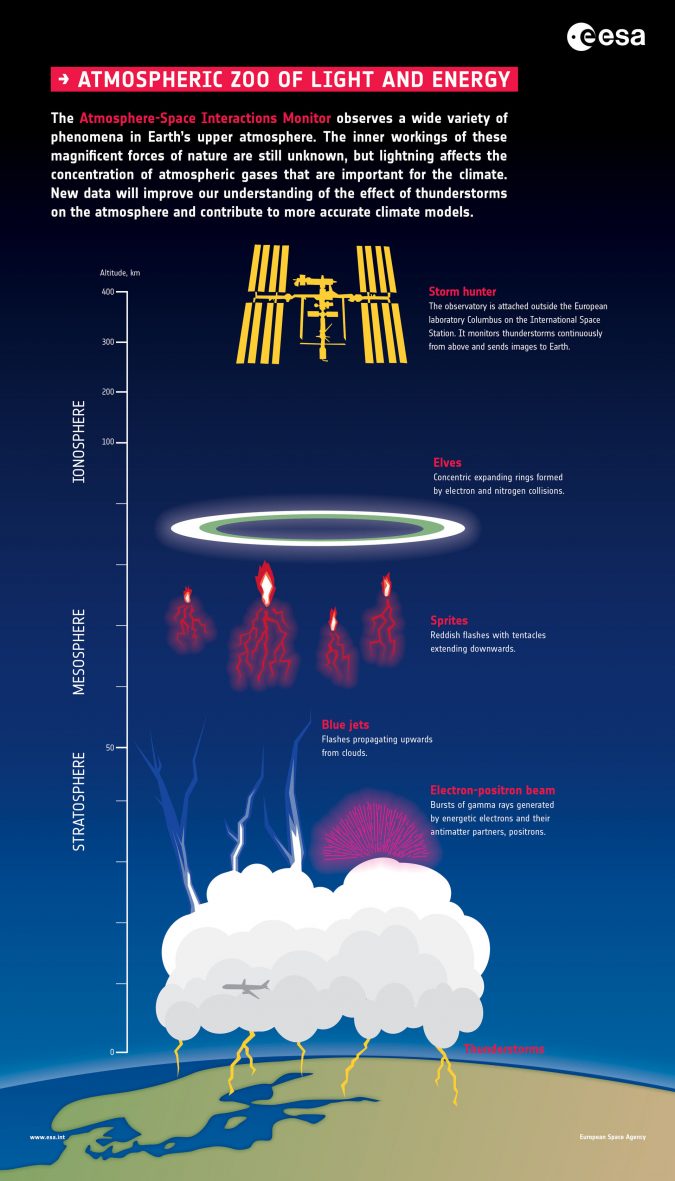
As it turns out, there are a lot of things left to discover. Things like blue jets, elves and red sprites. Bizarre-sounding things. Things that are very difficult to observe from the surface of the Earth. As a new Nature paper reports, however, the European Atmosphere-Space Interactions Monitor (ASIM) observatory on the International Space Station is helping scientists find answers.
Looking down on Earth’s weather from the International Space Station 400 km above, ASIM’s enhanced perspective is shedding new light on weather phenomena and their characteristics.
The collection of optical cameras, photometers and an X- and gamma-ray detector was installed on the Space Station in 2018. It is designed to look for electrical discharges originating in stormy weather conditions that extend above thunderstorms into the upper atmosphere.
And now, ASIM’s findings have been published in Nature as front-page article. The paper describes a sighting of five intense blue flashes in a cloud top, one generating a ‘blue jet’ into the stratosphere.
A blue jet is a form of lightning that shoots upwards from thunderstorm clouds. They can reach as far 50 km into the stratosphere and last less than a second. The space storm-hunter measured a blue jet that was kicked off with and intense five 10-microsecond flash in a cloud near the island of Naru in the Pacific Ocean.
The flash also generated equally fantastic-sounding ‘elves’. Elves are rapidly expanding ring of optical and UV emissions at the bottom of the ionosphere. Here, electrons, radio waves and the atmosphere interact to form these emissions.
Capturing these phenomena using the highly sensitive ASIM tools is vital for scientists researching weather systems on Earth. The observations hold clues to how lightning is initiated in clouds and investigators think these phenomena could even influence the concentration of greenhouse gasses in Earth’s atmosphere, underscoring once more how important it is to find out exactly what’s going on above our heads.
Astrid Orr, ESA’s Physical Sciences Coordinator for human and robotic spaceflight says, “This paper is an impressive highlight of the many new phenomena ASIM is observing above thunderstorms and shows that we still have so much to discover and learn about our Universe.
“Congratulations to all the scientists and university teams that made this happen as well as the engineers that built the observatory and the support teams on ground operating ASIM – a true international collaboration that has led to amazing discoveries.”